Welding is the fabrication process of joining similar or dissimilar metals with or without the application of heat and pressure. The process of joining two materials with the application of intense heat which melts the parts together and allowing them to cool is known as fusion.
If the filler material used is the same as the base material then it is known as homogeneous welding otherwise it is heterogeneous welding.
How Welding machine works
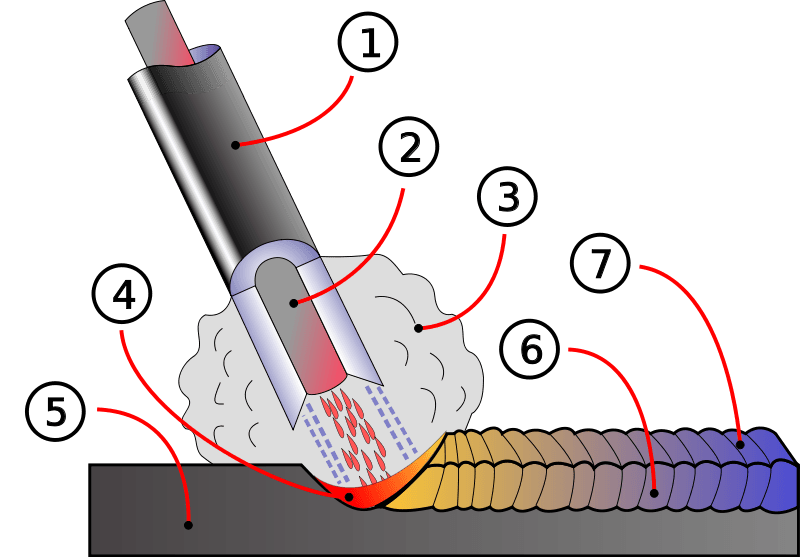
Diagram of arc and weld area, in metal arc welding.
1. Coating Flow
2. Rod
3. Shield Gas
4. Fusion
5. Base metal
6. Weld metal
7. Solidified Slag
For Welding to happen we need either heat, pressure, or both heat and pressure.
During welding, the material around the area that needs to be joined is heated up to its melting temperature by means of various welding methods which fuses both the material together with or without the help of filler material and allow them to cool up to ambient temperature.
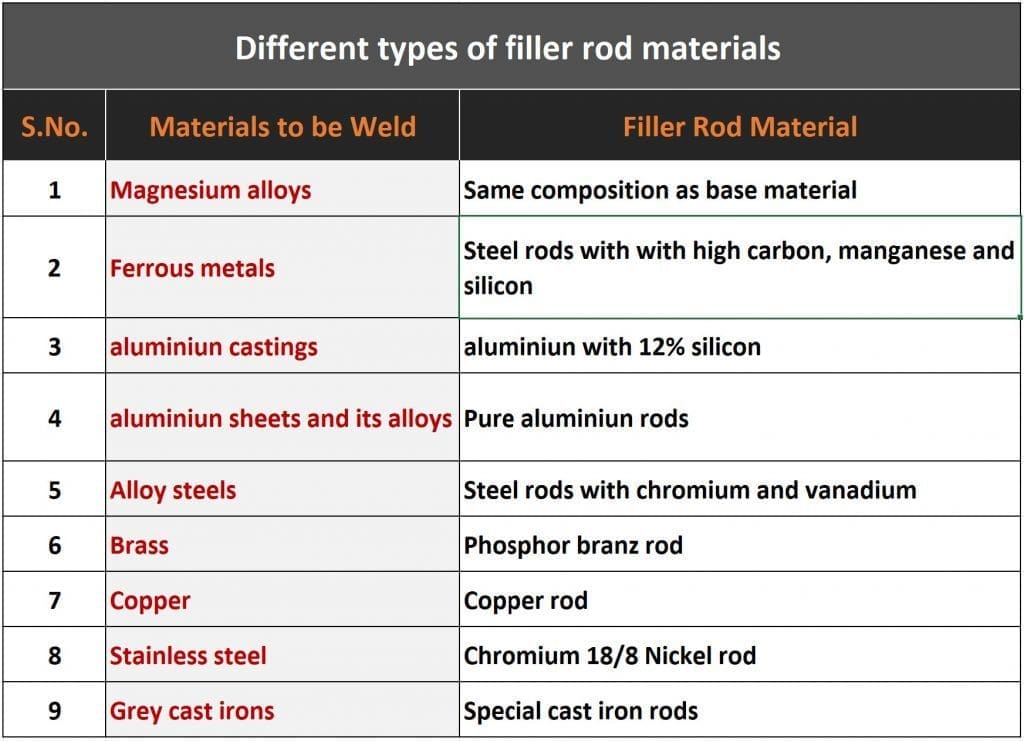
The weld area is generally fused with filler rods or wire ( thin flux coated/ non coated metal rods of the same material as base metal or different from base metal) to join both materials as it provides excess metal deposition for the joining process with alloying and shielding properties. In many weldings, shielding gases are used as an alternative to flux.
Most common Welding types & Process
1- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
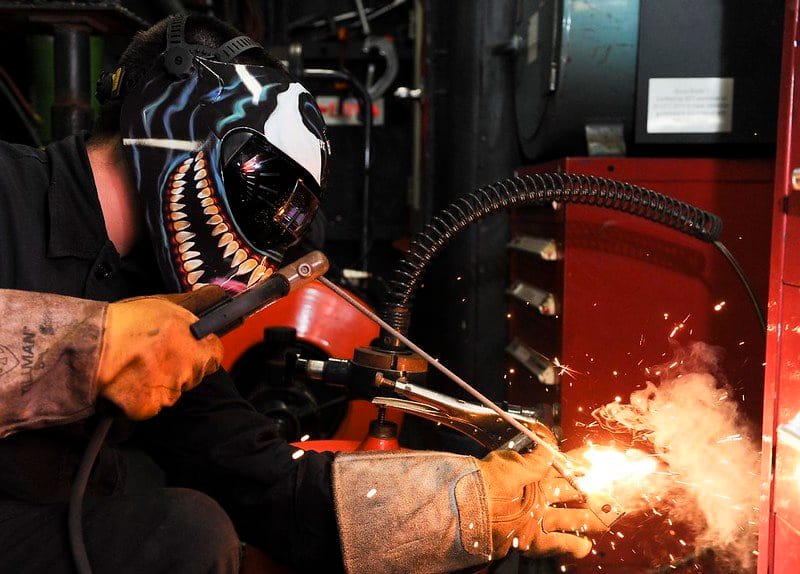

In a shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) the electric arc is generated by touching the tip of a coated electrode against the workpiece and then withdrawing it quickly to a distance sufficient to maintain the arc.
The arc is retained due to the potential difference between the electrode and the base metal.
The larger the air gap the higher will be the potential difference, if the air gap becomes too large the arc will be extinguished.
Note:
- The current to generate proper arc generally ranges from 50 amperes to 300 Ampere, the current may be DC or AC.
- The temperature in the core of the arc ranges between 6000 to 7000 degree Celsius
2- Metal Inert Gas Welding (MIG)
Metal inert gas welding (MIG) is also known as Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) In this, the weld area is shielded by an atmosphere of inert gases, the inert/shielding gases are organ, helium, carbon dioxide, or various gas mixtures.
MIG welding is an automatic system where electrodes are present in a form of spool wire.
In MIG welding the consumable bare wire is fed automatically through a nozzle along with shielding gas into the welding arc.
Note:
- MIG welding is used to weld stainless steel, copper, Mg, aluminum, Ni alloys in automobile and aircraft industries.
- MIG welding is suitable to weld a variety of ferrous and nonferrous metals and it is used extensively in metal fabrication and the automobile industry.
3- Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (TIG)
Tungsten inert gas welding (TIG) is also known as Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), generally used as manual welding.
In TIG welding a non-consumable tungsten electrode will be used to generate the arc and the additional filler rod is used, which is fused to the weld zone by the arc generated through the tungsten electrode.
To increase the thermal resistance of tungsten, alloying elements like Thorium and Beryllium are added.
Note:
It is generally used to weld aluminum and magnesium alloys in the automobile and aerospace industries.
4- Gas (Oxy-Acetylene) Welding
Gas welding consists of two cylinders, an oxygen cylinder, and Acetylene (Fuel) cylinder.
In gas welding, high-temperature flames are used to melt the surface of a material that needs to be welded.
High-temperature flames are produced by the reaction of acetylene gas with oxygen. The flux may be used to deoxidize and cleanse the weld metal.
Note:
The oxygen cylinder is black in color and the acetylene cylinder is red in color, always make sure that the valves of the oxygen cylinder are made of brass whereas in the acetylene cylinder valves are made of steel because if copper is used with acetylene then it will react and form copper acetylene, which is highly explosive in nature
There are generally Three Types of of flames used in gas welding-
- Neutral Flame
- Carburizing Flame
- Oxidizing Flame
Each flame has their own temperature range and applications.
5- Spot and Seam Welding
Spot and seam welding is a type of resistance welding where the heat required for welding is produced by the means of electrical resistance across the two components which need to be joined.
In spot welding, materials that need to be joined are held between the two electrodes under pressure, due to indentation (high pressure), there will be no gap at the interface of both the material.
So when a high current is passed, there will be maximum resistance at the interface which results in a sudden rise in temperature and fusion.
The working principle of both spot welding and seam welding is the same, the only difference is the shape of the electrode. The electrodes in seam welding are in the form of rollers or wheels as compared to water-cooled straight electrodes in spot welding.
Seam welding is generally used to obtain leak-proof joints.
6- Hyperbaric Welding
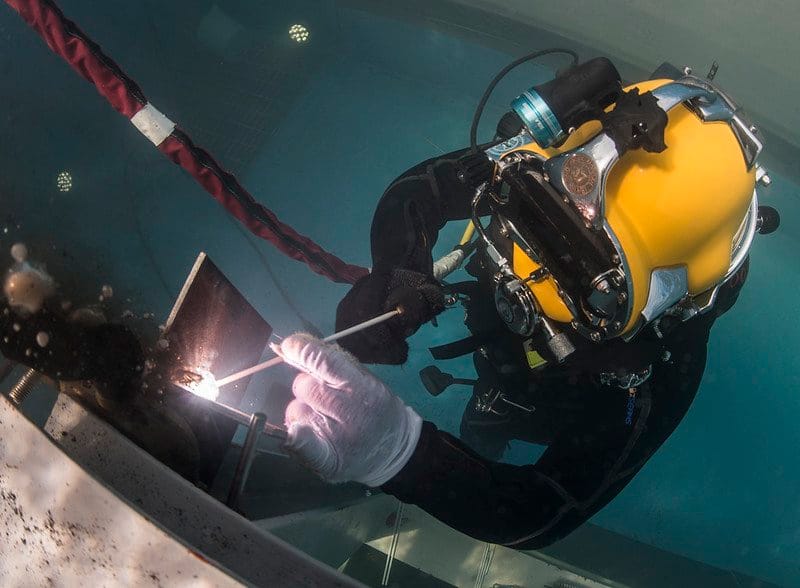

Hyperbaric welding is a type of welding which is performed at elevated pressures generally it’s underwater.
It can be used in both wet and dry conditions, if used in a dry environment it is known as hyperbaric welding, and if fused in a wet environment it is known as underwater welding.
There can be multiple applications of hyperbaric welding but It is generally used to repair ships, Offshore oil containers, pipelines, etc.
In underwater welding the driver and electrode are directly exposed to water surroundings, The electrodes of the divers are generally powered by 300-450 amps depending on the depth of weld and deposition rate.
A diver uses waterproof flux coated electrodes with a constant current type of transformer as it is manual welding.
7- Laser Welding
Laser beam welding is a concentrated coherent light beam, impinges at the desired spot to melt the area and weld the metal.
Laser beam welding is generally used in electronic companies to weld aluminium and copper where the level of precision and accuracy is very high
The most useful laser for welding is the laser in which the lasing medium is a mixture of CO2, nitrogen, and helium in a ratio of 1:1:10
There are two limitations of laser beam welding:
- Highly reflective material cannot be weld.
- The initial setup cost is very high.
Welding Transformers
To produce the necessary heat for welding generally, two types of welding transformers are used-
1- Constant Current type transformer
It is used in a type of manual welding where the arc length cannot be controlled so arc current is controlled by a transformer, which means that if the distance increases between the ARC and base material the transformer will increase the current but if the arc comes too close to the base material the transformer will reduce the current.
2- Constant Voltage type transformer
It is generally used in automatic or semi-automatic welding, It has a flat volt-ampere characteristic curve through with a slight drop.
If the load in the circuit changes, the power source automatically adjusts its currents output to satisfy the requirements.
The constant voltage power system has its greatest advantage when the current density of the electrode wire is high.
Why Welding Electrodes are Coated with Flux
When molten metal is exposed to air, it absorbs oxygen and nitrogen, and becomes brittle or is otherwise adversely affected.
A slag cover is needed to protect molten or solidifying weld metal from the atmosphere. This cover can be obtained from the electrode coating.
Electrodes are coated with materials like clay which includes silicate binders and powdered materials such as oxides, carbonates, chlorides, metal alloys, and cellulose.
Advantages of using flux coated electrodes
1- Used to stabilize the arc.
2- To act as a shielding element against the surrounding atmosphere.
3- To control the rate at which electrodes melts.
4- To protect the weld against the formation of oxides, nitrides, and other inclusions.
5- To add alloying elements to the weld zone for enhancing the properties of the joining.
6- Smooth weld metal surface with even edges.
7- It also provides the de-oxidizers to prevent the weld from becoming brittle and getting cracked.
Note:
The deposited electrode coating for slag must be removed after each pass in order to ensure a good weld.
8- Minimum spatter adjacent to the weld.
9- Easier slag removal.
How to select what Welding electrode/rod to use
Types of welding electrode-
1- Bare Coated Electrode
Bare coated electrodes are generally used in automatic and semi-automatic welding machines, they are not coated with flux material and they are generally present in a form of spool wire which is generally attached to the machine so it needs continuously an environment of inert/shielding gas which prevents the weld area from getting contaminated.
It is generally used in TIG welding and MIG welding.
2- Light coated Electrode
Light coated electrodes are used in both automatic and manual welding. A light coating is applied on the surface of electrodes by a process of spraying, washing, dipping, brushing, tumbling, or wiping.
The light coating on electrodes improves the characteristics of arc stream and stability.
3- Heavy coated or shielded arc Electrodes
Heavy coated electrodes are generally used in manual welding.
The coating on the electrodes is generally done by either extrusion or dipping process.
It is generally used in Shielded metal arc welding.
Electrodes are generally 2.5mm to 6.5 mm in diameter and 300 to 470 mm in length.
Concept of Welding Polarity
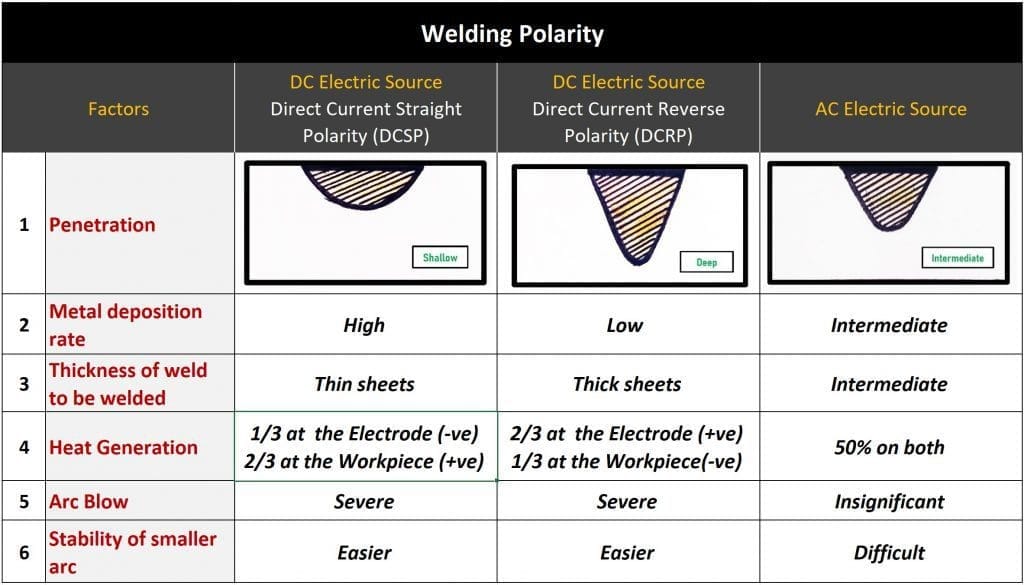
In Welding there are two types of polarity-
1- Direct current straight polarity (DCSP)
In direct current straight polarity, the electrode is connected to the negative terminal and workpiece to the positive terminal due to which 1/3 of the heat is generated on the workpiece and 2/3 of the heat generation is on electrode, which makes the electrode melt at a higher rate into the weld arc and forms high weld deposition.
Note:
It is generally used for thin metal sheets where a lesser depth of penetration is required with a high metal deposition rate.
2- Direct current reverse polarity (DCRP)
In direct current reverse polarity, the electrode is connected to the positive terminal and workpiece to the negative, due to which 1/3 of the heat is generated on the electrode and 2/3 of heat is generated on the workpiece which makes the workpiece extremely hot and allows the electrode to achieve a high depth of penetration.
Note:
It Is generally used for thick metal sheets where a high depth of penetration is required with less metal deposition rate.
Best Type of Welding to weld Aluminum
TIG (Tungsten Inert gas welding) is generally the best suitable option for welding aluminium and magnesium alloys with direct current reverse polarity (DCRP) option because in straight polarity, due to high-temperature oxide formation is severe which will not allow the electrons to transfer from the electrode to the workpiece.
While using reverse polarity we are getting excess depth of weld so if high depth of weld is not the requirement then you can switch to AC source to weld Al and Mg alloys.
Aluminium Welding
Best methods to weld Aluminium
Is the welding process harmful to our skin, eyes, and body?
Welding is harmful to our body if proper safety measures are not taken into consideration.
The basic safety measures are-
1- Welding should not be done in an enclosed space, the welding area should be properly ventilated by an exhaust system because during welding harmful gases are produced, if inhaled directly can harm the lungs and cause breathing problems.
2- Use a welding helmet or glasses to prevent injuries from the high-intensity arc, which can directly harm our eyes if we directly see into the core of arc or gas flame.
3- Use welding gloves to protect your hand from getting burned by heat generated during welding.
4- Use insulated electric wirings with a proper earthing system to prevent electric shocks.
5- Setup fire extinguishers at specific locations that are most prone to catching fires.
Note:
Make sure to understand the complete procedure of how to operate the welding machine before using it and follow all the safety measures while performing welding.













