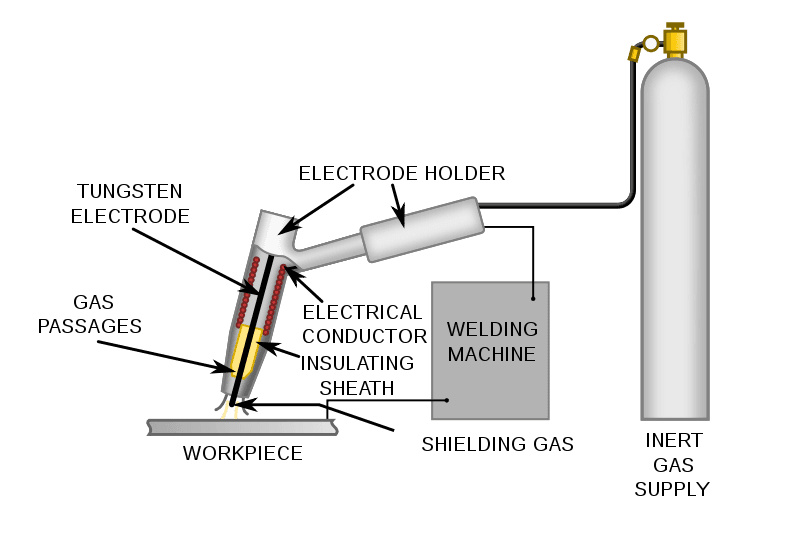
TIG welding is also known as Tungsten inert gas welding (GTAW), it is a technique in which a non-consumable tungsten electrode is used to generate the arc which then generates intense heat causing filler material to melt and deposit on the weld area.
Liquid metal in the weld pool is protected by providing the inert gas atmosphere, applied through a cup-shaped gas at the end of the welding torch where the electrode is centrally positioned.
Argon is most commonly inert gas used in TIG welding.
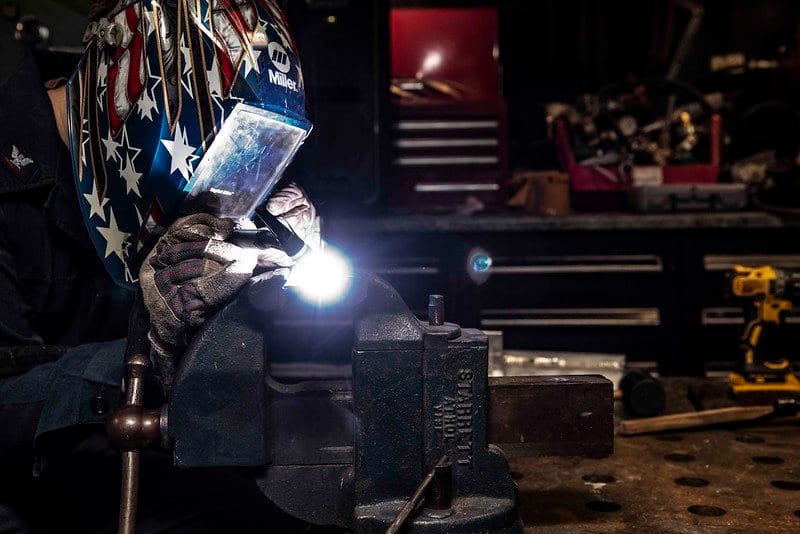

How TIG welding works & performed
The welding is performed due to the intensely heated arc generated between a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a workpiece.
The arc is provided by the filler material (excess material similar or dissimilar from the base material) and the atmosphere of inert gases.
The molten weld pool is protected by the atmosphere of inert gases such as – helium, neon, argon, nitrogen and carbon dioxide, etc.
Note:
- Nitrogen gas is preferred for welding copper.
Steps to perform TIG welding
1- Power on supply of the welding torch along with the opening of the valve of the inert gas cylinder.
Note:
- Generally, most pressure regulators have two stages of regulators. The first stage is a fixed pressure regulator which releases the gas from the cylinder at constant intermediate pressure, despite the reason that the pressure in the cylinder is falling as gas is continuously consumed for welding.
- The second stage of pressure regulator controls the pressure reduction from the intermediate pressure to the low outlet pressure (remaining pressure).
2- Power supply will be AC or DC depending on the workpiece material.
Note:
- For Welding aluminium and magnesium alloys we use AC power supply
3- To generate the arc, touch the tip of a tungsten electrode against the workpiece and then withdraw it quickly to a distance sufficient to maintain the arc.
4- Once the arc is generated you can use filler material for welding as the heat generated by the arc will melt a portion of filler material as we move along the weld.
Note:
- Flow of Filler material rod is is controlled manually.
TIG Welding diagram
TIG welding polarity
Polarity in welding determines the connection of positive and negative terminals with workpiece and electrode depending on the material and weld requirement.
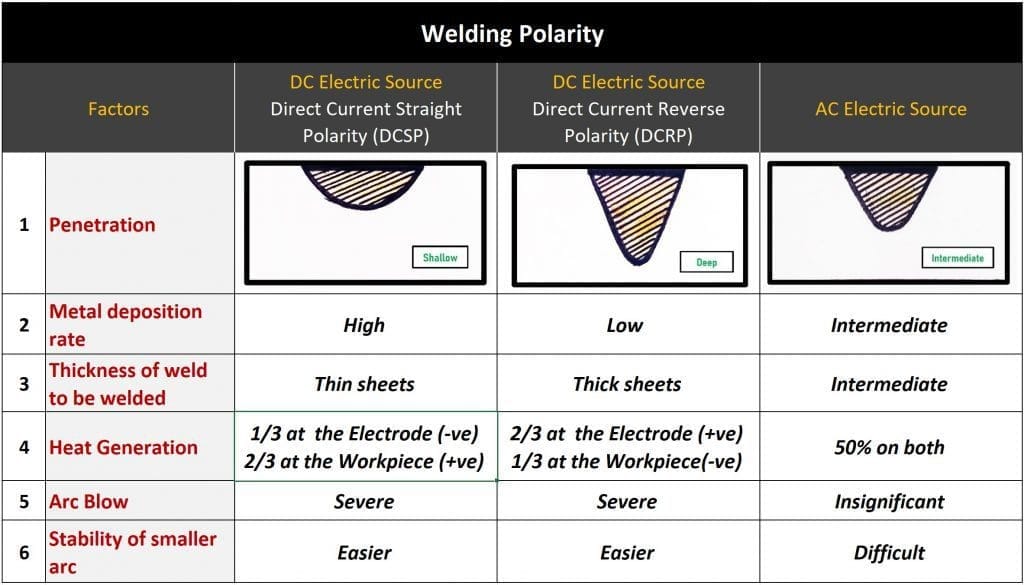
AC Power Source
If an AC power source is used then both straight and reverse polarity will occur one after the other in each cycle, for half of the cycle the electrode will be negative and the base plate will be positive, and in the other half, the electrode will be positive and the base plate will be negative.
The number of cycles depends on the frequency of power supply.
DC Power Source
If DC power source is used there can be two set of polarity-
- Direct current straight polarity (DCSP)
- Direct current reverse polarity (DCRP)
Direct current straight polarity will be used for all the metals except aluminum and magnesium alloys because straight polarity generates high temperature, due to which oxide formation is severe hence this will not allow the electrons to flow properly from the electrode.
So, to weld aluminum and magnesium alloys either direct current reverse polarity is used for AC power source is used.
For better understanding refer to the above image.
Parts and components of TIG Welding
1- Welding Electrodes in TIG Welding

- Non-consumable tungsten electrodes are used to generate the arc.
- To increase the thermal resistance of tungsten, alloying elements like thorium and beryllium are added.
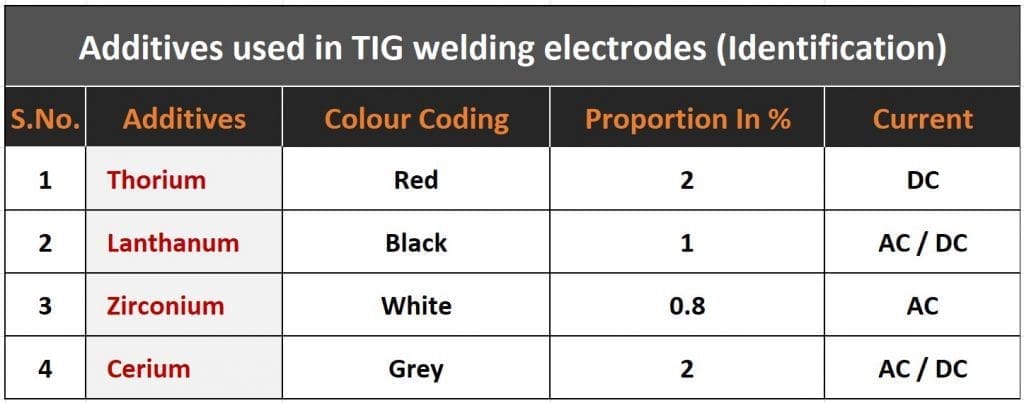
- The materials of the electrode should provide a combination of the following characteristics:-
- High melting point
- Good thermal conductivity
- Low electrical resistance
- Good emission of electrons
Note:
Tungsten is the best suitable material used for this welding as a non-consumable electrode because it has a melting point of 3370 degrees Celsius and the property of heat conduction is almost similar to aluminum.
2- Welding Torch
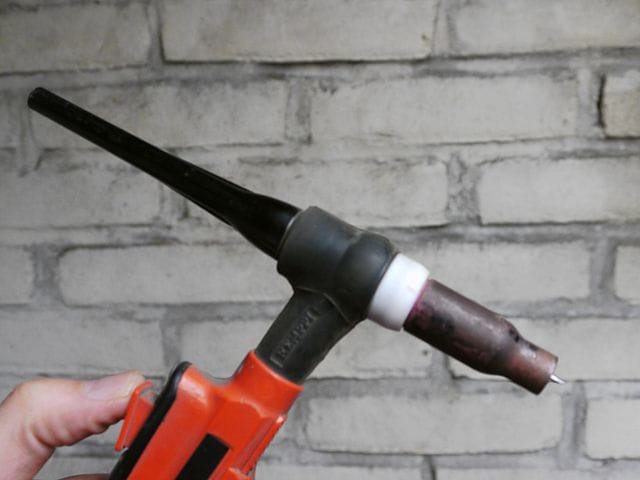

The function of a welding torch is to hold the tungsten electrode in its center and allow inert gasses to pass through it.
There are mainly two types of welding torches used-
- Air-cooled welding torch with a maximum operating range of 200 ampere
- Water-cooled welding torch with a maximum operating range of 400 ampere
3- Welding Power Source
TIG welding is normally carried out using a DC power source with either positive polarity or negative polarity, the selection of polarity depends on the base material and weld requirements.
Whereas aluminum and magnesium and generally welded using a DC power source.
Since it’s manual welding, a constant current type transformer will be used with an open-circuit voltage of about 80 V.
4- Shielding or Inert gases
- The shielding or inert gas is used to protect the molten weld pool from the atmospheric gases.
- There are various inert gases used such as- Helium, neon, argon, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide
Material and their Shielding gases:
- Steel, unalloyed, low alloyed steel
- Argon
- Argon with (helium/hydrogen)
- A mixture of nitrogen/hydrogen
- Aluminum and its alloys
- Argon with the addition of helium
- Copper and its alloys
- Argon for thickness up to 6 mm
- Helium or helium with 35% or argon for the thickness of more than 6 mm
- Titanium
- Extremely pure helium or argon, if welding thick sections use helium.
The shielding gases provide welds with very high quality and surface finish with better arc stability.
5- Filler Wire
Fillers for TIG welding are used in a form of wire which is fed into the arc by the help of hand or mechanically.
The filler materials used in welding are supplied in a form of rods about 1 meter long in length, filler rods used are barely coated but in some cases, they are lightly coated with flux.
When to use TIG Welding (APPLICATIONS)
1- Used for joining pipes and welding tubes in heat exchangers.
2- For welding aluminum and magnesium alloys in the automotive and aerospace industries.
3- For welding of copper and its alloys.
4- Used for various repair applications such as cars, heat exchangers, boilers, pipes, rods, tubes, etc.
TIG welding is best suited for which material
- Tungsten inert gas welding was primarily invented to weld alloys of aluminum and magnesium.
- Extremely thin material can also be welded up to a minimum thickness of 3mm.
- For welding of non-alloyed steels or low-alloy steels with argon as a shielding gas.
- For welding of copper and its alloys with a combination of helium and organ as a shielding gas.
Note:
Tungsten inert gas welding can be used to weld almost all kinds of metals but it is not preferred for materials other than aluminum and magnesium because there are various other cheap welding alternatives present in the market to weld those metals.
TIG Welding Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Formation of excellent arc stability due to the presence of shielding gases.
- Excellent control over welding results.
- Best suitable for welding thin sheets of light metals such as aluminum, magnesium alloys, and copper.
- Thin sheets can be welded up to 3mm.
- Leak Proof joints can be obtained.
Disadvantages
- Not suitable to weld materials other than Al and Mg as loss of inert gases makes it a costly process when it comes to weld other metals.
- It cannot be used to weld zinc and lead.
- It is manual welding so the moment of filler material is controlled by hand, this process requires skill.
- Thick welds can not be generated.
How much do TIG welders make
The income of TIG welders depends on the location, country, pay scale criteria, hours of work, working profile, etc.
The average salary of TIG welders in the United States is around 17 to 30 dollars per hour.
It can vary from country to country based on the government and working policies.







